Let’s start by defining subrogation. “Subrogation is defined as ‘the substitution of another person in the place of a creditor, so that the person in whose favor it is exercised succeeds to the rights of the creditor in relation to the debt.’” (Blankenship v. Estate of Bain, (Tenn. 1999) 5 S.W.3d 647, 650). “[S]ubrogation is a doctrine that is generally governed by equitable principles rather than terms of the contract giving rise to the subrogation claim. We noted that the primary purpose of subrogation is ‘to prevent either the unjust enrichment of the insured through a double recovery or a windfall benefit to the principal tortfeasor.’” (Abbott v. Blount County (Tenn. 2006) 207 S.W.3d 732, 734).
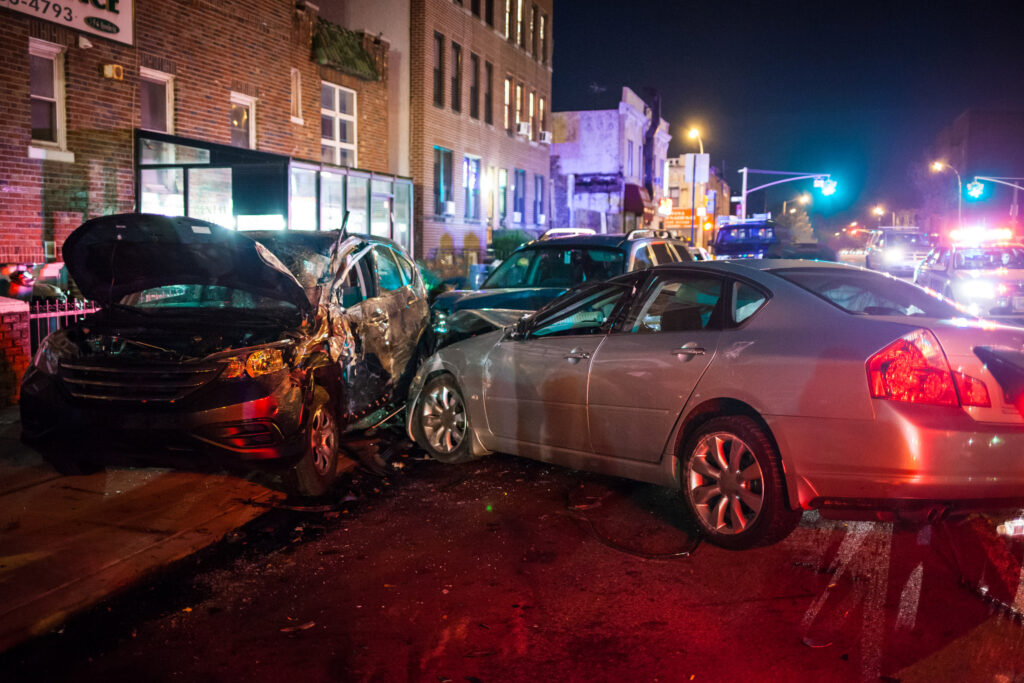
So how does this work in Insurance? Well, there are three people involved in these types of cases. You have 1. The Insurance Company; 2. The Insured; and 3. The Tortfeasor. Your basic subrogation scenario is the Tortfeasor causes a car accident and damages an Insured. The Insurance Company pays the Insured to make him whole and then stands in the Insured’s shoes and sues the Tortfeasor.
Ok so what does the Insured have to prove against the Tortfeasor? They must prove negligence. The “Court has long defined negligence as the ‘want of ordinary care.’” (Lawson v. Hawkins Cnty. (Tenn. 2023) 661 S.W.3d 54, 61). “To prove negligence, a plaintiff must establish ‘(1) a duty of care owed by the defendant to the plaintiff; (2) a breach of that duty; and (3) a causal relation between the injury to the plaintiff and the defendant’s breach of his duty of care.’” (Id. at 61). If the Insurance Company can prove the Tortfeasor was negligent then the Insurance Company can recover damages.
If you have found yourself in a car accident and you are sued in subrogation it is important to find counsel. There are defenses that can be raised.